Speed Up Your Internet By Tweaking DNS Server Address
Last month, Google and several DNS resolution and content delivery network (CDN) companies joined forces to enhance Internet speed
by localizing domain name system (DNS) resolution responses. This move
should reduce delays in downloading online content due to failure to
find the closest CDN server of the website being visited. All you need
to do is change the DNS server address of your computer to enjoy the
benefits of the new DNS resolution standard.

Internet Speed : The EDNS – Client – Subnet Standard
This
is the name of the new domain name resolution protocol forged by
Google and its industry partners. Under this standard, your computer’s
location will be taken into account when finding the server of the web
site being visited. But isn’t that how the current system works?
Definitely not.
The process of
downloading a website begins with a search of the IP address of its
host or cache server. This is the job of the DNS. Your ISP’s DNS server
is the one that initiates the IP search.
A
website could have copies stored in many servers located in various
places, each having its own IP address. These servers are operated by
CDN providers. Websites with copies stored in many CDN cache servers
are therefore associated with many IP addresses. The DNS server of your
ISP attempts to find the server closest to itself, not the one closest
to your computer. What if your ISP server and your computer are 10
cities apart? Who wants to waste Internet speed due to poor DNS resolution standard?
The
edns-client-subnet standard is developed to address the inefficiency
of the current DNS resolution standard in order to minimize download
latency. This standard requires DNS servers to know the location of the
client so that the CDN cache server closest to it can be located. This
will guarantee that the Internet surfer will be directed to the cache
server closest to his current location, and not the location of his ISP
DNS server, thereby minimizing the dampening effect of geographic
distance on Internet speed.
The
edns-client-subnet standard is only implemented by a number of CDN
companies. As of now, you need to use the server addresses of either
Google Public DNS or Open DNS to experience the new DNS resolution
standard.
IPv4 Addresses of Google Public DNS:
- 8.8.8.8
- 8.8.4.4
IPv6 Addresses of Google Public DNS:
- 2001:4860:4860::8888
- 2001:4860:4860::8844
OpenDNS
- 208.67.222.222
- 208.67.220.220
- 208.67.222.220
- 208.67.220.222
Find and Change Your Current DNS Address to Boost Internet Speed
For Mac OS X
- Go to System Preferences-> Network.
- Select the connection you want to configure. Then click Advanced.
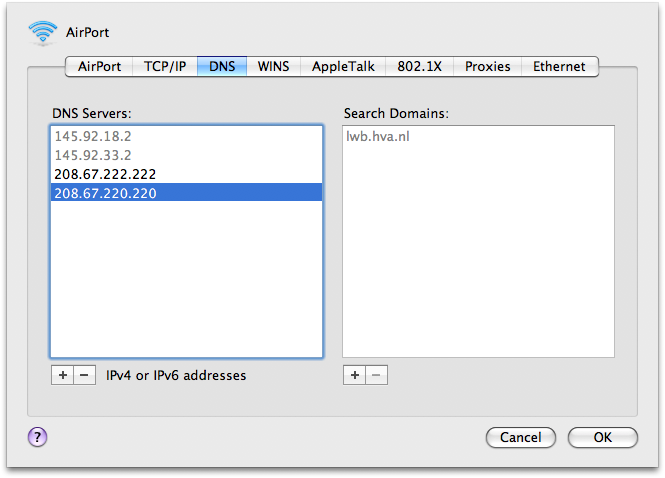
- Click
the DNS tab on the menu bar. Click the plus sign at the bottom of the
screen to add the DNS server address of Google Public DNS or OpenDNS.
Click Apply and OK.
For Vista and Windows 7
- Go to Start Menu-> Control Panel-> Network and Sharing Center.
- Choose Manage Network Connections for Vista or Change Adapter Settings for Windows 7.
- Right click the network connections you want to change, then choose Properties.
- Click the Networking tab on the menu bar.
- Choose either Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) or Internet Protocol Version 6 and go to Properties.
- You will see a new window like the one below.
- Choose Use the Following DNS Server Address. Add either the Google Public DNS or OpenDNS IP addresses.

Let’s
hope the new standard gains more acceptance from ISPs and other CDN
and DNS companies.You wouldn’t see improvements in Internet speed if
the websites you are visiting are not using the servers of CDN
companies participating in this initiative. Hope you all enjoy good
Internet Speed.











0 comments:
Post a Comment
Please share your valuable feedback and sugession panda.alok@hotmail.com